Categories are essentially telling Google, “Show my business for these types of searches.” Think of them as the digital version of yellow page categories, they determine which section your business appears in.
Your primary category has the strongest influence on showing up in Google for the right terms people search with, while secondary categories expand your visibility without diluting your main focus. Get this combination right, and you’ll appear in more relevant searches than your competitors.
Finding Your Perfect Primary Category
Your primary category should represent your main business function, the primary service or product that drives most of your revenue. This category appears publicly on your Google Business Profile, so it needs to be both accurate and strategic.
For example:
- A pizza restaurant that also serves pasta would select “Pizza Restaurant” (not the more general “Restaurant”)
- A general dental practice would choose “Dentist” (not the more specific “Pediatric Dentist” unless that’s their specialty)
- A women’s clothing boutique would select “Women’s Clothing Store” (not just “Clothing Store”)
But how do you know which category will perform best? Here’s our insider research strategy:
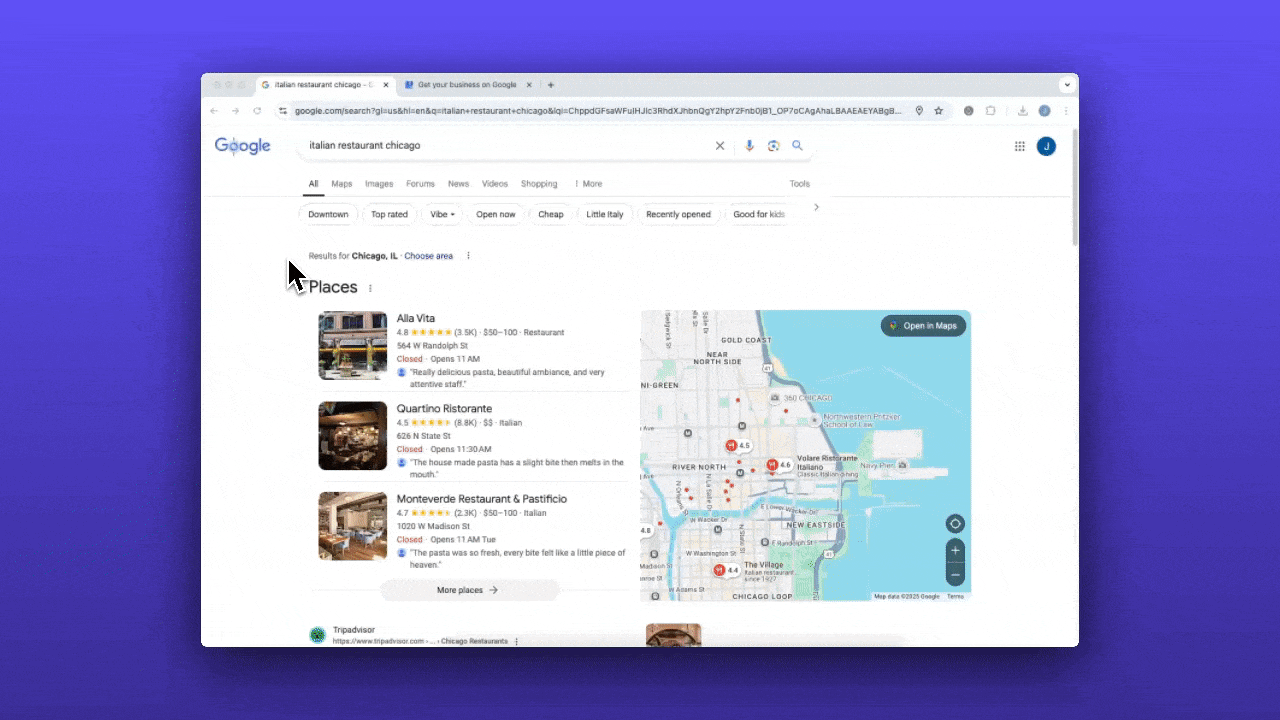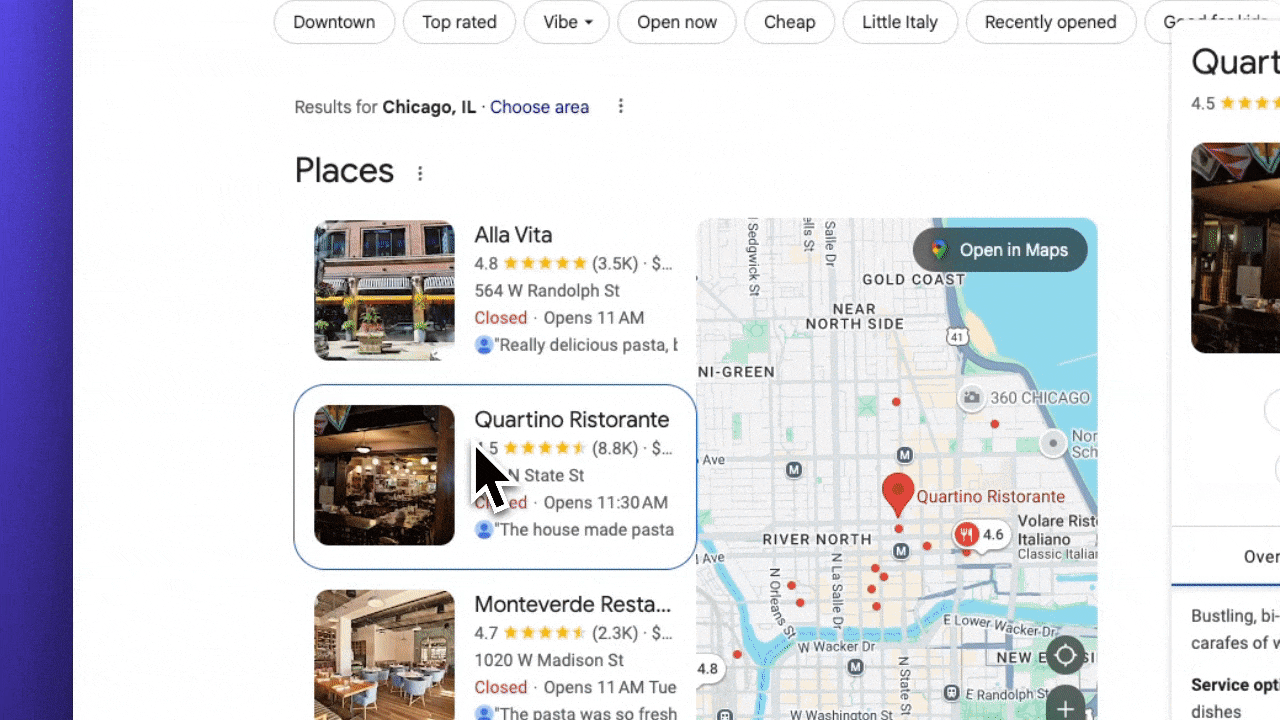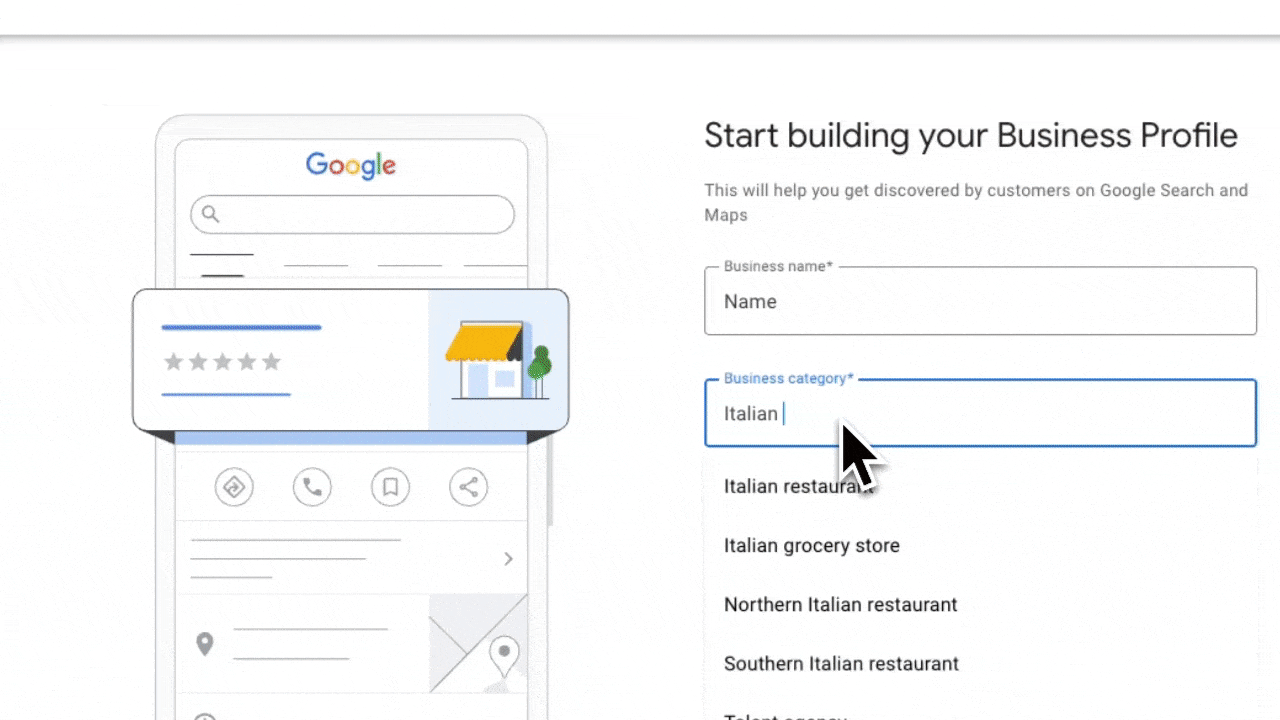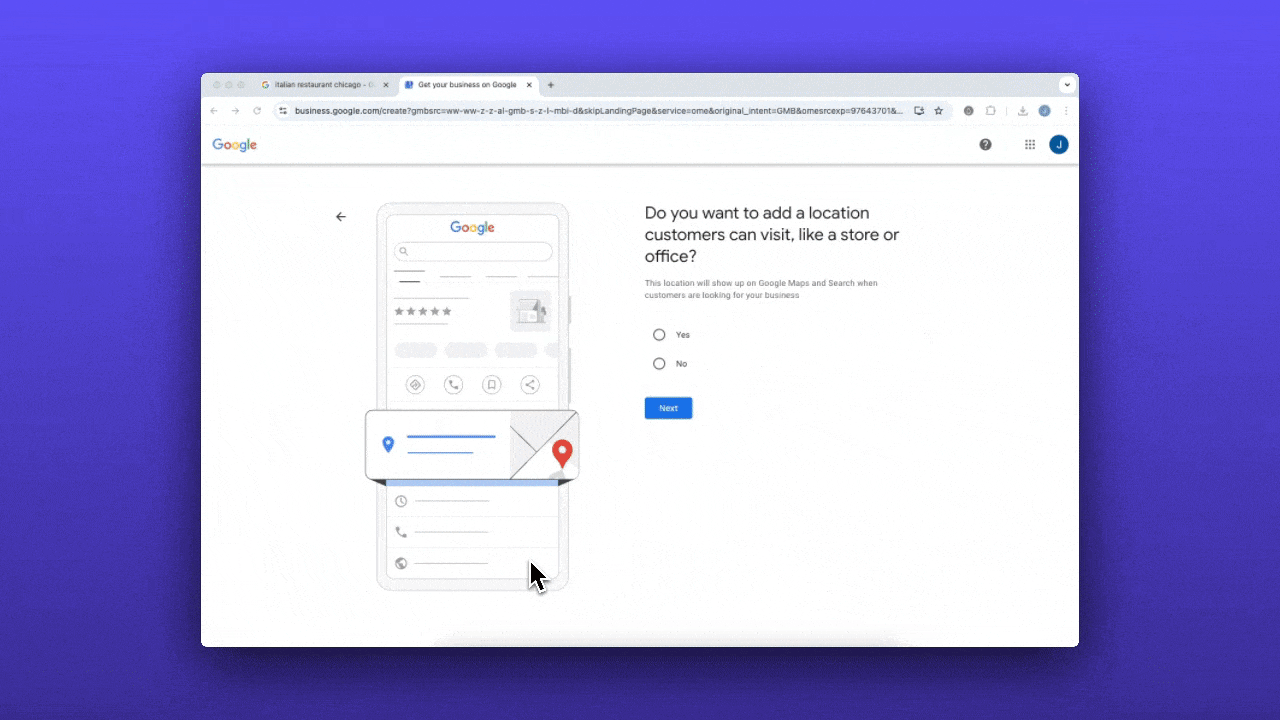
- Spy on top performers - Search for your main products or services using the terms important to you and see what categories the top 3 businesses have selected. You can view a competitor’s primary category right on their Google Business Profile.
- Go specific, but not too niche - When picking a category for your business on Google, you want to be specific enough to attract the right people but not so specific that you miss potential customers.
Think of it like this - if you run an Italian restaurant, choosing just “Restaurant” as your category is too general. You’ll be competing with every taco place, sushi bar, and burger joint in town. But going with something super-specific like “Sicilian Restaurant” might be too narrow unless that’s truly your specialty. You might miss people searching for general Italian food.
Your best bet? Choose “Italian Restaurant” - it’s specific enough to tell Google exactly what kind of food you serve but broad enough to appear when people are looking for pasta, pizza, and other Italian favorites.
- Match your core offering - Your primary category should align with how most customers describe your business and what they type in browsers to find you (NOT what you think they type).
Doubling-Down the Effect with Secondary Categories
Here’s where you can get more specific without risking your main visibility. You can add up to 9 secondary categories, but resist the temptation to add irrelevant ones just to appear in more searches. Google can hide profiles that try to game the system.
Let’s look at a real estate agency example. Their primary category might be “Real Estate Agency,” with secondary categories like:
- Property Management Company
- Real Estate Consultant
- Commercial Real Estate Agency
- Apartment Rental Agency
Each of these represents a legitimate aspect of their business, creating a complete picture of their services for Google.
Category Selection Strategy by Industry
Different industries require different approaches to category selection:
For Service Businesses:
- Primary: Your main service type (plumber, electrician, house cleaning service, landscaping)
- Secondary: Specific service specialties, seasonal services, and complementary services (emergency plumber, Christmas light installation service, handyman, pool maintenance service)
For example, Violet’s Plumbing would select “Plumber” as the primary, then add “Water Heater Installer,” “Bathroom Remodeler,” and “Emergency Plumber” to capture different customer needs.
For Restaurants/Food:
- Primary: Your main cuisine or food type (Mexican restaurant, coffee shop, bakery)
- Secondary: Dining style, specific meal types, atmosphere types, service methods (fine dining, brunch, sports bar, delivery restaurant)
Real-world example: Bella Napoli might choose “Italian Restaurant” as their primary category, then add secondary categories like “Pizza Restaurant”, “Lunch Restaurant”, “Dinner Restaurant” and “Delivery Restaurant” to highlight different aspects of their business that customers search for.
For Retail:
- Primary: Your main store type (women’s clothing, bookstore, pet store, jewelry store)
- Secondary: Specific product categories, specialty departments, or service add-ons (shoe store, fashion accessories, watch repair service)
In a real-world example, Main Street Cycles might select “Bicycle Shop” as their primary category, with secondary categories like “Bicycle Repair Shop,” “Sporting Goods Store,” “Electric Bicycle Shop,” and “Bicycle Rental Service” to capture their full business offering.
For Professional Services:
- Primary: Your main professional designation (attorney, accountant, marketing agency)
- Secondary: Specialty areas, client types, service delivery methods (divorce attorney, business attorney, virtual accountant)
Smith & Partners Law Firm would use “Attorney” as primary, then add specific practice areas like “Personal Injury Attorney,” “Criminal Justice Attorney,” and “Estate Planning Attorney” as secondaries.
Keeping Categories Fresh
Categories aren’t set in stone, they should evolve as your business does. Google regularly adds new, more specific categories, so check monthly for minor updates and review quarterly for major category expansions that might better describe what you do. When your profile stays updated, it accurately reflects your business offer and remains competitive.
Also, review your categories when:
- Your business adds or changes services
- You notice competitors ranking for keywords you’re missing
- Seasonal offerings become available (like “Christmas Tree Farm” during winter)
- You see a drop in visibility for important keywords
By selecting and maintaining your categories in the best shape, you’ll gain a significant edge in local search visibility. Next, let’s look at another crucial factor, visual content optimization.
Welcome back to Localo Complete Local SEO Course! Your Google Business Profile is created and verified - you’re making amazing progress!
Today, we’re diving into something that might seem simple but actually determines whether customers find you or your competitors. We’re talking about category selection, and trust me, getting this right can be the difference between being invisible and dominating your local market.
Why do categories determine which searches you appear in?
Categories are essentially telling Google, “Show my business for these types of searches.” Think of them as the digital version of yellow page categories - they determine which section your business appears in when people search.
Here’s what makes this so powerful: your primary category has the strongest influence on showing up in Google for the right terms people search with. Secondary categories expand your visibility without diluting your main focus. Get this combination right, and you’ll appear in more relevant searches than your competitors.
This isn’t just about being found - it’s about being found by the right people at exactly the right moment. When someone searches for your specific type of business, categories are what put you in front of them instead of letting them discover your competitor down the street.
How do you find your perfect primary category?
Your primary category should represent your main business function - the primary service or product that drives most of your revenue. This category appears publicly on your Google Business Profile, so it needs to be both accurate and strategic.
Here’s how to think about it: a pizza restaurant that also serves pasta would select “Pizza Restaurant” rather than the more general “Restaurant.” A general dental practice would choose “Dentist” rather than the more specific “Pediatric Dentist” unless that’s truly their specialty. A women’s clothing boutique would select “Women’s Clothing Store” rather than just “Clothing Store.”
The key is being specific enough to attract the right people while staying broad enough that you don’t miss potential customers. You want to hit that sweet spot where people searching for exactly what you offer can find you easily.
What’s the insider research strategy for choosing categories?
Here’s our insider research strategy that most businesses never think to do. First, spy on top performers. Search for your main products or services using the terms important to you and see what categories the top three businesses have selected. You can view a competitor’s primary category right on their Google Business Profile.
Second, go specific, but not too niche. When picking a category for your business on Google, you want to be specific enough to attract the right people but not so specific that you miss potential customers.
Think of it like this - if you run an Italian restaurant, choosing just “Restaurant” as your category is too general. You’ll be competing with every taco place, sushi bar, and burger joint in town. But going with something super-specific like “Sicilian Restaurant” might be too narrow unless that’s truly your specialty. You might miss people searching for general Italian food.
Your best bet? Choose “Italian Restaurant” - it’s specific enough to tell Google exactly what kind of food you serve but broad enough to appear when people are looking for pasta, pizza, and other Italian favorites.
Third, match your core offering. Your primary category should align with how most customers describe your business and what they actually type in browsers to find you.
How do secondary categories multiply your visibility?
Here’s where you can get more specific without risking your main visibility. You can add up to nine secondary categories - but resist the temptation to add irrelevant ones just to appear in more searches. Google can hide profiles that try to game the system.
Let’s look at a real estate agency example. Their primary category might be “Real Estate Agency,” with secondary categories like Property Management Company, Real Estate Consultant, Commercial Real Estate Agency, and Apartment Rental Agency.
Each of these represents a legitimate aspect of their business, creating a complete picture of their services for Google. This approach captures different customer needs while maintaining focus on their main business function.
What category strategies work best for different industries?
Different industries require different approaches to category selection, so let me break this down by business type.
For service businesses, your primary should be your main service type - plumber, electrician, house cleaning service, landscaping. Secondary categories cover specific service specialties, seasonal services, and complementary services like emergency plumber, Christmas light installation service, handyman, or pool maintenance service.
For example, Violet’s Plumbing would select “Plumber” as the primary, then add “Water Heater Installer,” “Bathroom Remodeler,” and “Emergency Plumber” to capture different customer needs.
For restaurants and food businesses, your primary should be your main cuisine or food type - Mexican restaurant, coffee shop, bakery. Secondary categories cover dining style, specific meal types, atmosphere types, and service methods like fine dining, brunch, sports bar, or delivery restaurant.
Real-world example: Bella Napoli might choose “Italian Restaurant” as their primary category, then add secondary categories like “Pizza Restaurant”, “Lunch Restaurant”, “Dinner Restaurant” and “Delivery Restaurant” to highlight different aspects of their business that customers search for.
For retail businesses, your primary should be your main store type - women’s clothing, bookstore, pet store, jewelry store. Secondary categories cover specific product categories, specialty departments, or service add-ons like shoe store, fashion accessories, or watch repair service.
Main Street Cycles might select “Bicycle Shop” as their primary category, with secondary categories like “Bicycle Repair Shop,” “Sporting Goods Store,” “Electric Bicycle Shop,” and “Bicycle Rental Service” to capture their full business offering.
For professional services, your primary should be your main professional designation - attorney, accountant, marketing agency. Secondary categories cover specialty areas, client types, and service delivery methods like divorce attorney, business attorney, or virtual accountant.
Smith & Partners Law Firm would use “Attorney” as primary, then add specific practice areas like “Personal Injury Attorney,” “Criminal Justice Attorney,” and “Estate Planning Attorney” as secondaries.
How do you keep your categories fresh and competitive?
Categories aren’t set in stone - they should evolve as your business does.
When your profile stays updated, it accurately reflects your business offer and remains competitive. Also, review your categories when your business adds or changes services, you notice competitors ranking for keywords you’re missing, seasonal offerings become available like “Christmas Tree Farm” during winter, or you see a drop in visibility for important keywords.
Here’s something most businesses miss: Google is constantly adding new categories that might be perfect for your business. That category that didn’t exist six months ago might now be exactly what you need to capture more relevant searches, so check monthly for minor updates and review quarterly for major category expansions that might better describe what you do.
What category mistakes can hurt your visibility?
The biggest mistake? Adding irrelevant categories just to appear in more searches. Google’s algorithms are smart enough to detect when businesses are trying to game the system, and the penalties can hurt your overall visibility.
Another common error is being too general with your primary category. Remember, your primary category is your most powerful tool for appearing in relevant searches. Don’t waste it on something too broad.
And here’s one that surprises many business owners: not updating categories when your business evolves. If you’ve added new services or shifted your focus, your categories should reflect that change.
By selecting and maintaining your categories strategically, you’ll gain a significant edge in local search visibility. Remember, this isn’t about tricking Google - it’s about accurately representing what your business offers so the right customers can find you.
In our next video, we’ll explore visual content that turns searchers into customers. We’ll dive into the photos and videos that make potential customers stop scrolling and start calling. Thanks for joining me today, and I’ll see you in the next video!
The websites and Google Business Profiles used throughout the course are for educational purposes only. We're not affiliated with these businesses and don't claim any endorsement from them. All trademarks belong to their owners. Some examples include visual changes (made with browser tools) to help illustrate the SEO concepts we're teaching. These edits are strictly local and illustrative of specific SEO concepts. They don't affect the original websites.




