Published
|Last updated
Https
Learn what HTTPS is and why it is so crucial for web browsers. Click and read more.
Published
|Last updated
Learn what HTTPS is and why it is so crucial for web browsers. Click and read more.
![What is HTTPS secure connection [Marketing Dictionary]](/assets/img/dictionary-background.webp)
What is Https
HTTPS ( Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) - This is a secure version of HTTP; this prevents interception and alteration of the transmitted data protocol on the web servers. HTTPS is a layer above transport layer security (TLS) at the presentation layer, so TLS keys are exchanged first, then the request. Due to security reasons and Google’s preference for HTTPS pages, more and more website owners are switching from plain HTTP sites to supporting HTTPS. Building an HTTPS site improves their visibility on the search engines. Using HTTPS connections increases the security of your personal data. Still, it does not encrypt all the information, like the IP address of your device or the name of the website you are visiting.
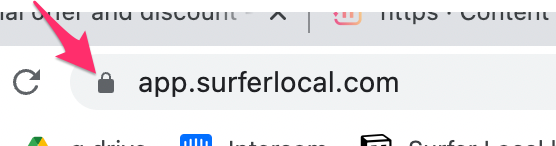
Using an HTTPS connection increases the security of your personal data, but it does not encrypt all the information, such as the IP address of your device or the name of the website you are visiting. Moreover, using encrypted websites will not protect us from being infected by viruses or phishing for confidential information if we send it through a form on phishing sites. HTTPS works well wherever user data is collected, such as online forums, social networking sites, and commenting sites.
❤️ Spread the word! ❤️
Found this guide valuable? Share it with your colleagues to help them boost their local marketing results too!
Powered by Localo 2026